"Time Wastes Too Fast": Jefferson’s Clocks
One of the most poignant of Jeffersonian artifacts is a 1782 scrap of paper with a quotation from the novel Tristram Shandy, written in Martha Wayles Jefferson’s hand but then taken up by her husband Thomas, as she was too weak to finish. Beginning with the phrase “time wastes too fast,” the snippet goes on to lament the fleeting nature of time for lovers about to be parted. Although this was a favorite passage from a favorite novel, Jefferson’s ideas about time were not always so romantic. In fact, Jefferson’s more scientific side is on full display at Monticello in a treasure-trove of timekeeping devices ranging from sundials to gongs, to various types of clocks.
If time is money, it is also order, control, efficiency, mathematics and physics: all concepts used by Jefferson to mold the world of his household and the enslaved inhabitants of his plantation. Many are familiar with the deservedly famous Great Clock at Monticello, which displays Jefferson’s ingenuity, love of precision (it has a hand that ticks the seconds!), and his desire to put the organizing principle of time at the very center of his estate. But let’s look at a few of the many timekeeping devices beyond the Great Clock and see how they impacted all those who lived at Monticello.
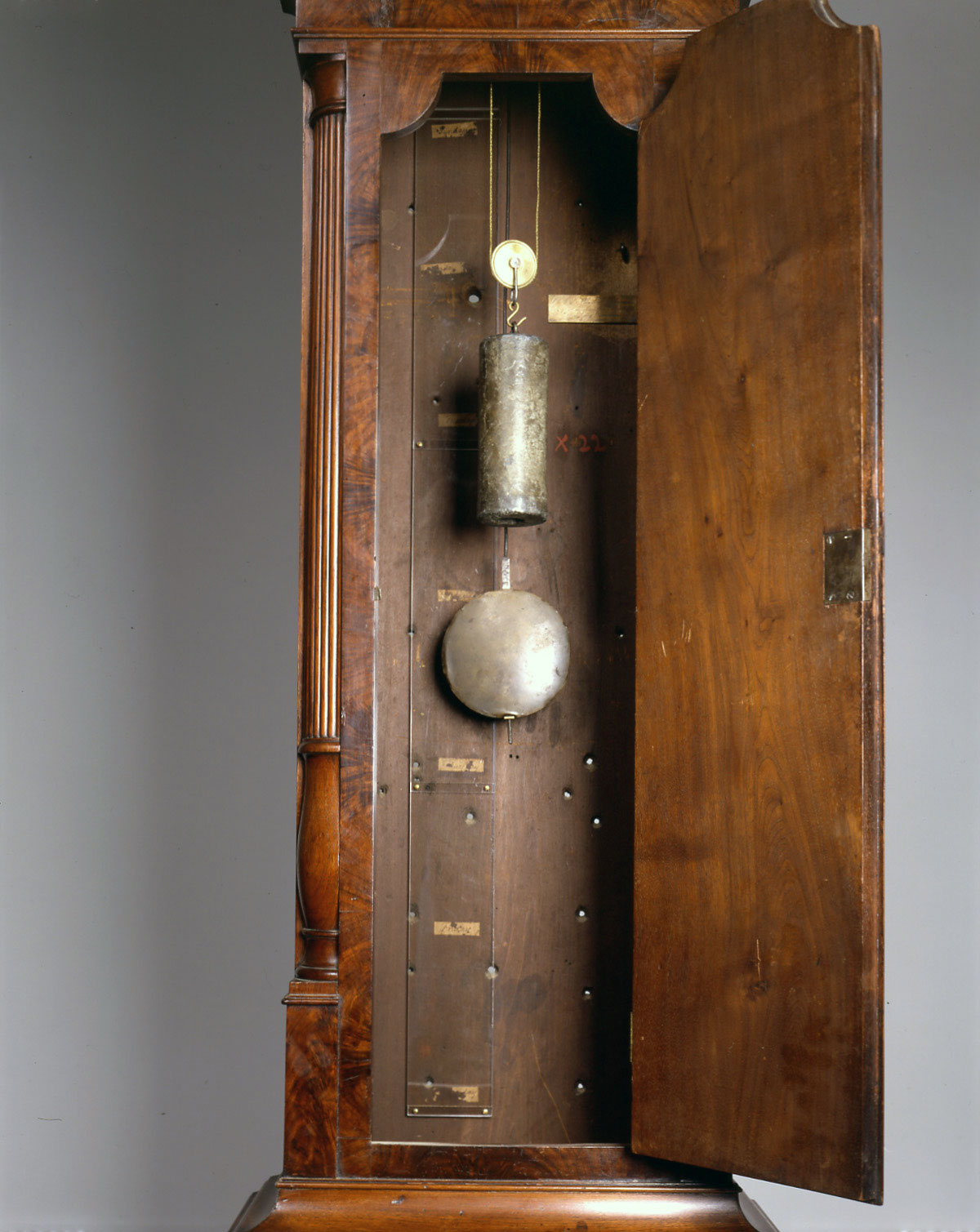

The interior of the astronomical clock, with the days of the week marked in similar fashion to the Great Clock in the Hall
Visitors to Monticello have always loved the Great Clock, but Jefferson’s favorite may have been the astronomical clock kept in his personal suite from 1812 onward. This one was the result of his desire since the 1770s to have an instrument so precise that it could be used in astronomical observations, such as charting eclipses. Because Jefferson planned to use it only for that purpose, this astronomical clock had no need for a chiming mechanism. Nor did it have an astronomical clock’s usual dials showing the relative positions of the sun, moon, planets, and constellations. In his directions to the maker, Jefferson specified that “no unnecessary labour [was] to be spent on mere ornament. [A] plain, but neat mahogany case will be preferred….” Although it may look quaint to modern eyes, this timepiece was very high-tech, of a type usually found in astronomical observatories and not in private homes.
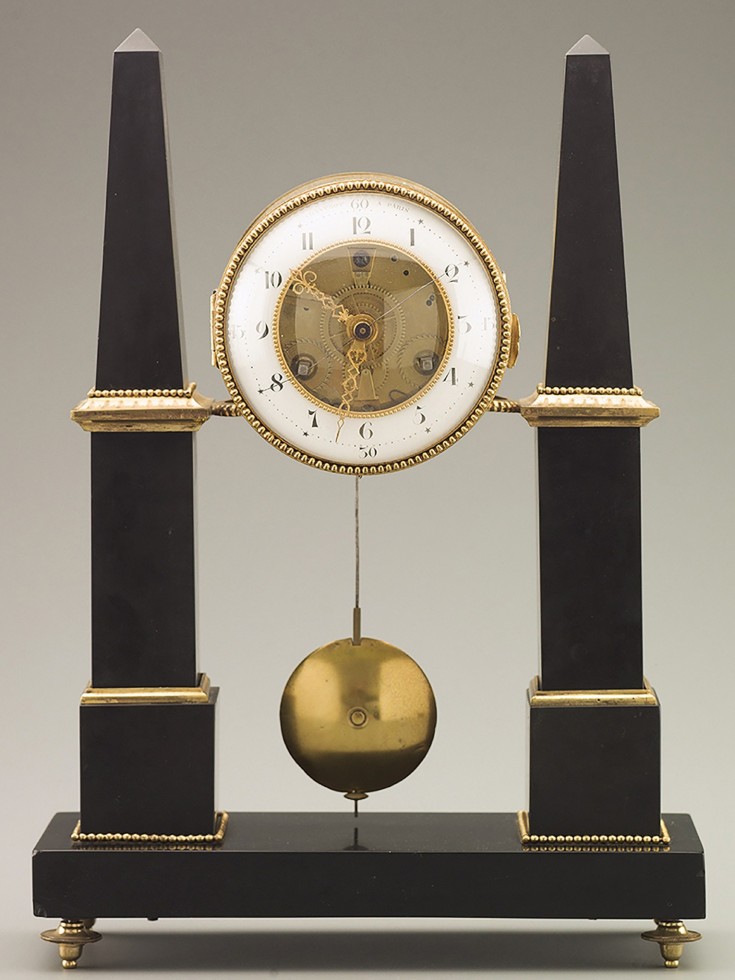
A small clock was very visible to Jefferson each morning as he arose “with the sun.” The spare, elegant marble and brass obelisk clock on the wall at the end of his bed was made in 1791 from Jefferson’s sketch and precise instructions, which featured the face suspended between two obelisks. The clock held such significance to Jefferson that after his death his daughter Martha called it the object “I should have prized beyond anything else.” The timeless obelisk form was persistently interesting to him, all the way to his self-designed obelisk-shaped grave marker.
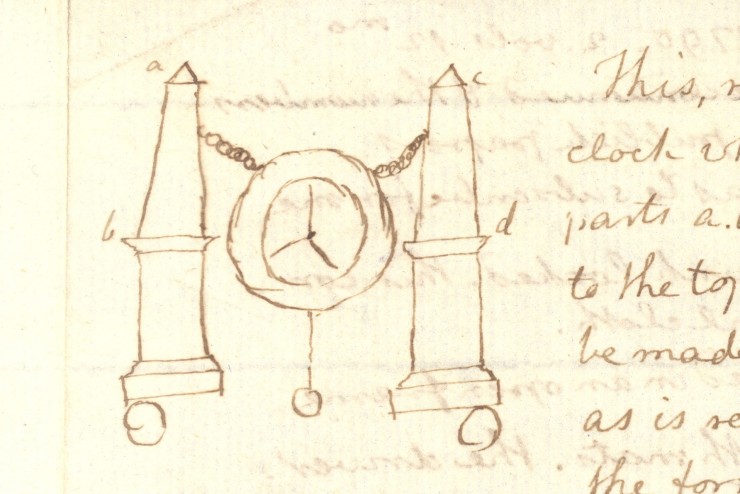
Jefferson’s 1790 sketch for his obelisk clock

Jefferson's Obelisk Clock

Weekly winding of Monticello's Great Clock

Thomas Jefferson and Clocks and Timepieces - Livestream




